IO流原理及流的分类
I/O是Input/Output的缩写, I/O技术是非常实用的技术,用于处理设备之间的数据传输。如读/写文件,网络通讯等。Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以 “流(stream)” ” 的方式进行。可以想象两个节点之间连接着一跟管子,两节点之间通过管子来传输数据,而数据在管子里就像是水流一样,从一节点流到另一个节点。
java.io包下提供了各种“流”类和接口,用以获取不同种类的数据,并通过 标准的方法输入或输出数据。
流的分类
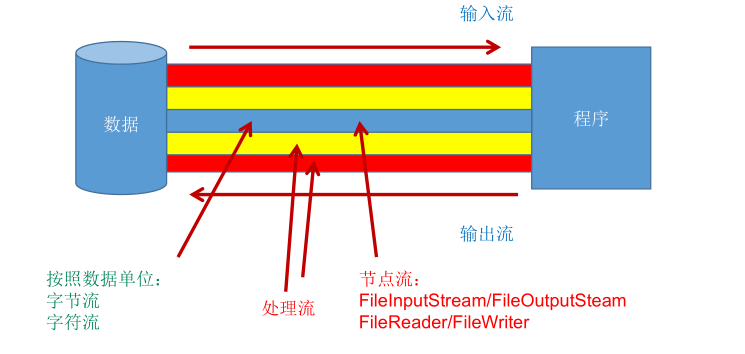
按操作数据单位不同分为:流字节流(8 bit) ,字符流(16 bit)。字节流是用来操作图形、音视频等文件,而字符流是用来处理文本文件的。
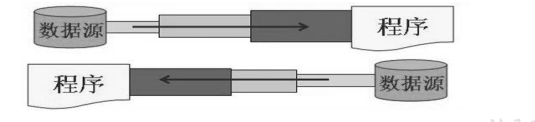
按数据流的流向不同分为: 输入流,输出流
按流的角色的不同分为:节点流,处理流
| 抽象基类 | 字节流 | 字符流 |
|---|---|---|
| 输入流 | InputStream | Reader |
| 输出流 | OutputStream | Writer |
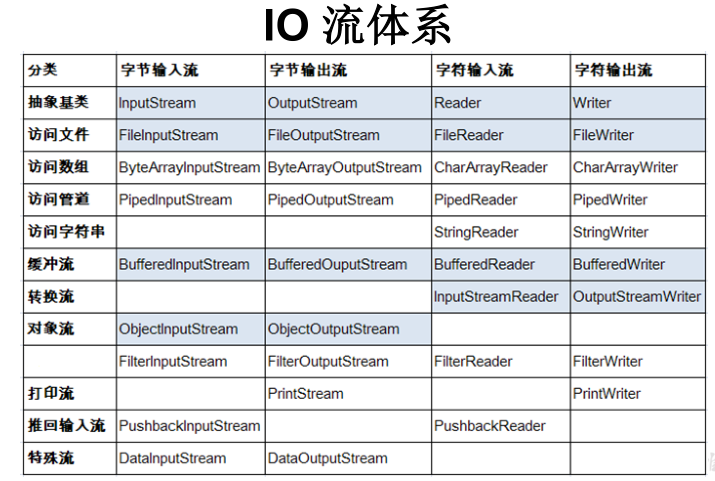
Java的IO流共涉及40多个类,实际上非常规则,都是从如上4个抽象基类派生的。由这四个类派生出来的子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名后缀
节点流和处理流
节点流:直接从数据源或目的地读写数据
数据流:不直接连接到数据源或目的地,而是“连接”在已存在的流(节点流或处理流)之上,通过对数据的处理为程序提供更为强大的读写功能。
IO流体系
InputStream & Reader
InputStream 和 Reader是所有输入流的基类。
程序中打开的文件IO资源不属于内存里的资源,垃圾回收机制无法回收该资源,所以应该件显式关闭文件IO资源。
inputStream
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
abstract int |
read() |
Reads the next byte of data from the input stream. |
int |
read(byte[] b) |
Reads some number of bytes from the input stream and stores them into the buffer array b. |
int |
read(byte[] b, int off, int len) |
Reads up to len bytes of data from the input stream into an array of bytes. |
void |
close() |
Closes this input stream and releases any system resources associated with the stream. |
Reader
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
abstract void |
close() |
Closes the stream and releases any system resources associated with it. |
int |
read() |
Reads a single character. |
int |
read(char[] cbuf) |
Reads characters into an array. |
abstract int |
read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) |
Reads characters into a portion of an array. |
int |
read(CharBuffer target) |
Attempts to read characters into the specified character buffer. |
OutputStream & Writer
关于输入的主要有三个方法:
- void write()
- void flush() 刷新此输出流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字节,调用此方法指示应将这些字节立
即写入它们预期的目标。 - void close() 关闭